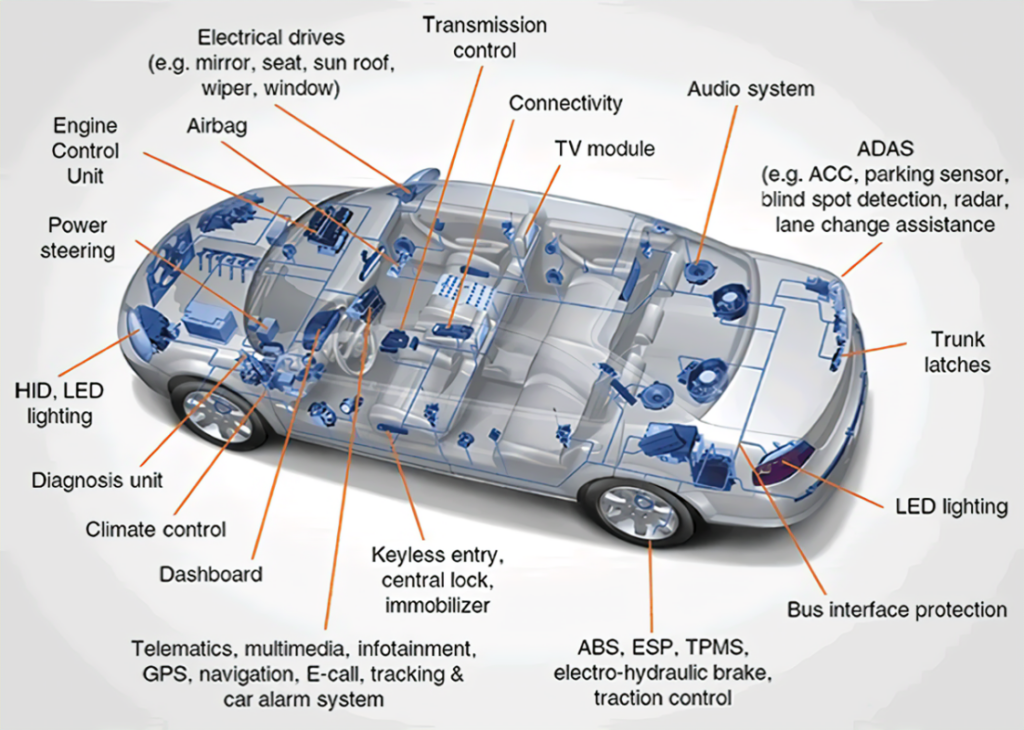
Automotive
Embedded systems control engine management, safety features, and infotainment systems in cars.
Each system is designed and programmed to do one job. For example, the airbag controller is designed to deploy the airbags in your car when it receives input from a sensor behind the front bumper in a collision.

Consumer Electronics
Kitchen appliances, smart TVs, and wearables all rely on embedded systems.
A microwave is a good example of an embedded system in your home. A microprocessor receives input from the user (when you push the buttons) and it controls the system to heat up your food according to the settings/time you chose.
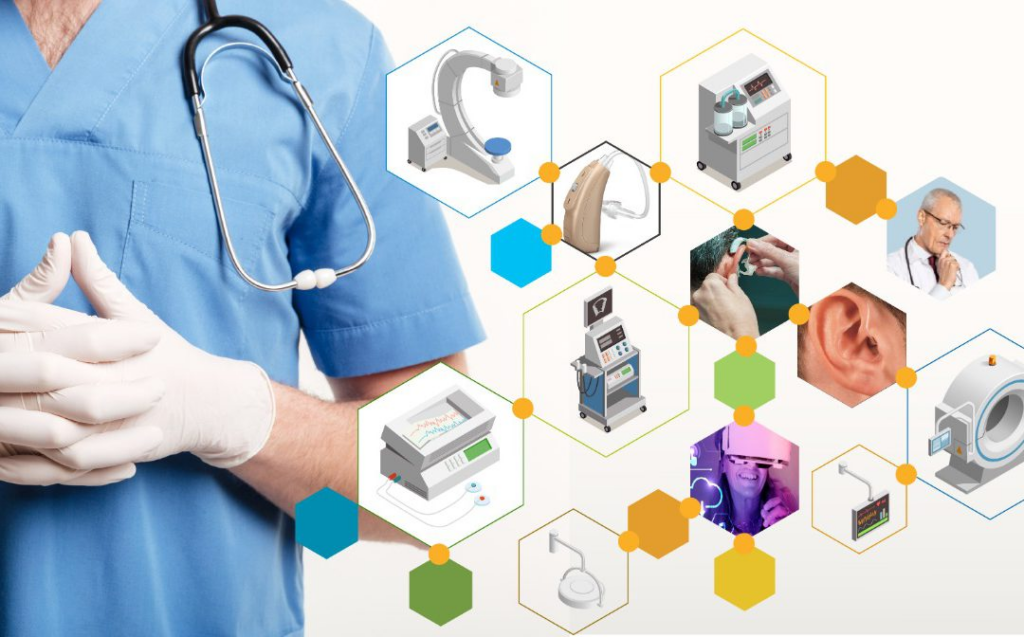
Healthcare
Medical devices like pacemakers and insulin pumps are powered by embedded systems.
A heart rate monitor in a hospital room is an embedded system that receives input from sensors connected to the patient and uses that information to produce and output on the screen that health care staff can read to monitor the patient. They are also often programmed to produce a warning signal in the event of a cardiac emergency.
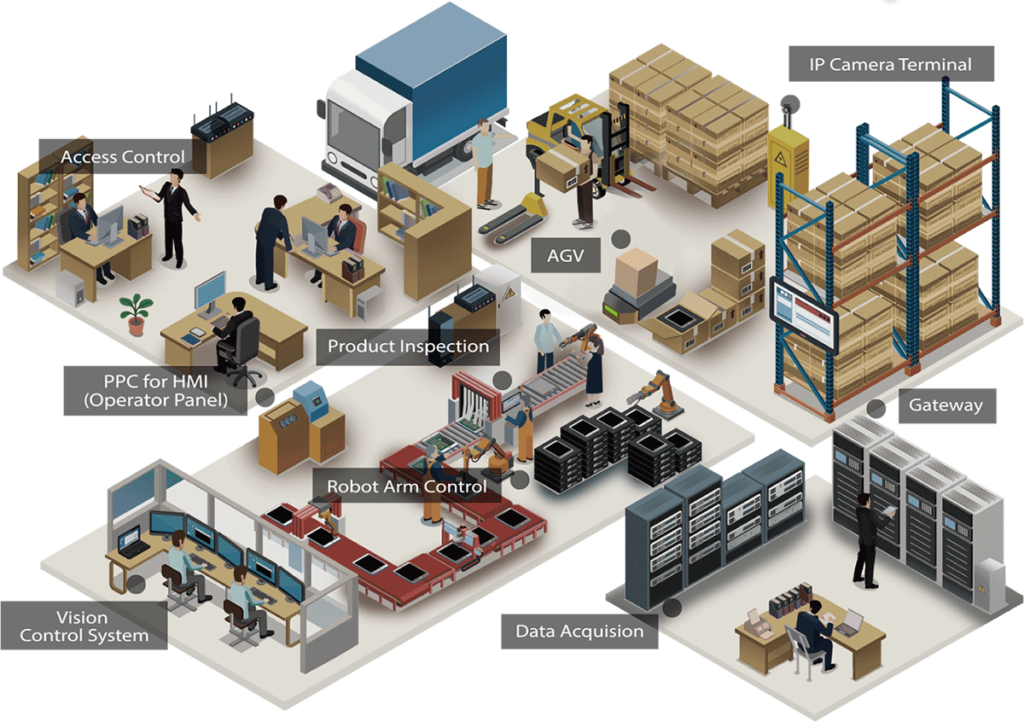
Industry and Manufacturing
Robots, CNC machines, and factory automation systems use embedded technology.
A great example of embedded systems in industry is a port. The containers are inspected and monitored, the cranes manage the inventory automatically, robotic cranes and shuttles are controlled from a remote location, and security systems monitor and notify personnel of issues, all with the help of embedded systems.

