Digital twins can be categorized into four main types, each serving a unique purpose and offering distinct benefits:
Component Twins: These are digital models of individual components or parts, such as motors, sensors, or valves. They provide detailed information about a component’s performance and behavior both in real-time and over time.
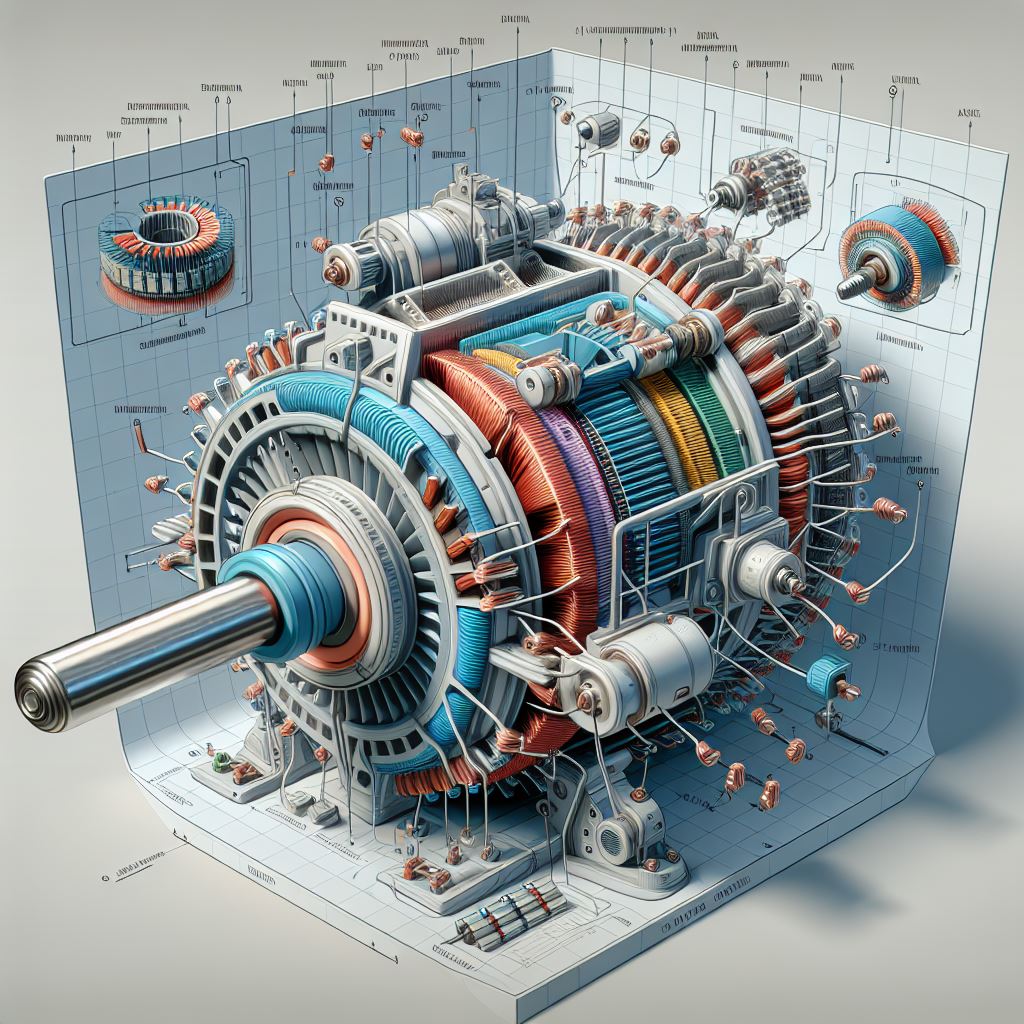
Asset Twins: These represent entire physical assets, like machines, vehicles, or buildings. Asset twins provide information on an asset’s operational status, performance data, and environmental conditions in real-time.

System Twins: These are digital models of entire systems or processes, such as a manufacturing line or a power grid. System twins allow organizations to monitor and analyze a system’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
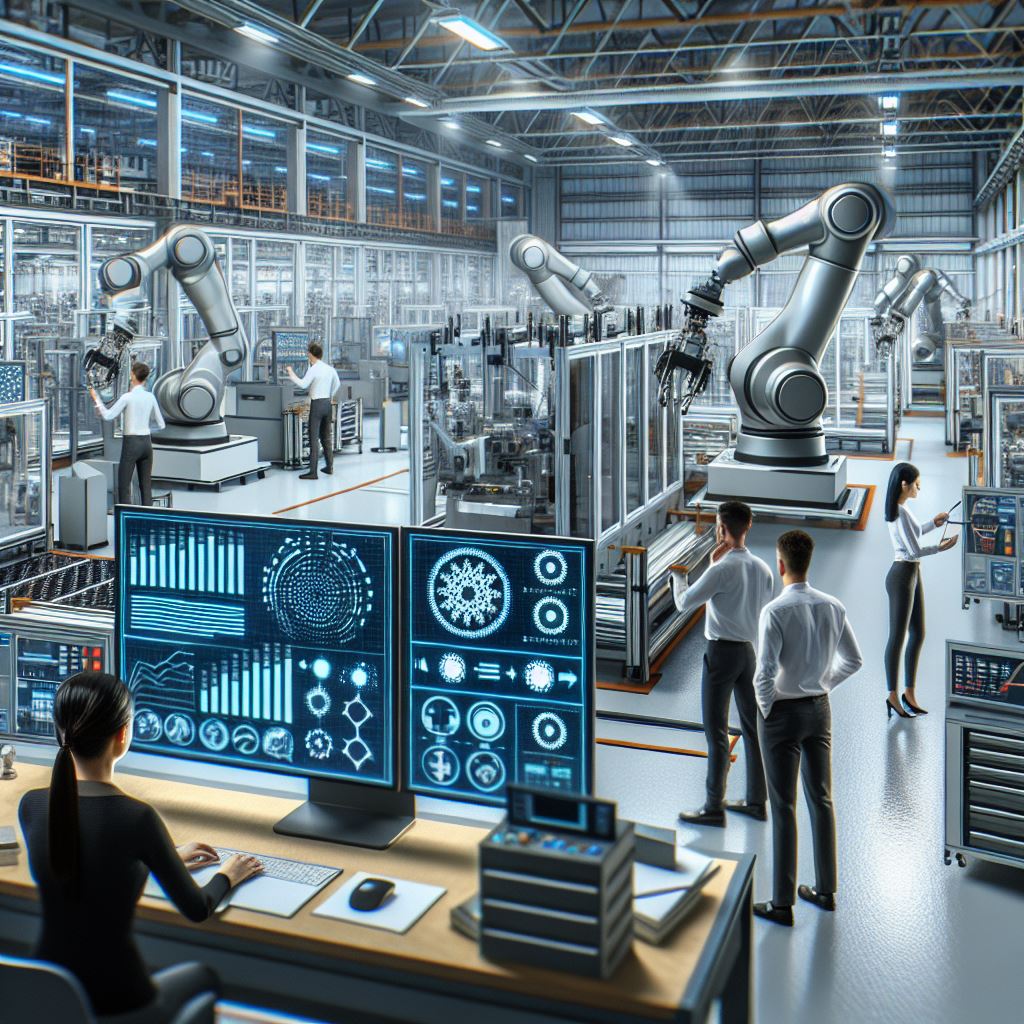
Process Twins: These represent entire business processes or workflows. Process twins provide detailed information on how processes operate, helping organizations optimize efficiency and improve outcomes.

Each type of digital twin plays a crucial role in enhancing the understanding, monitoring, and optimization of physical entities and processes across various industries.

