Types of 3D Printers
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
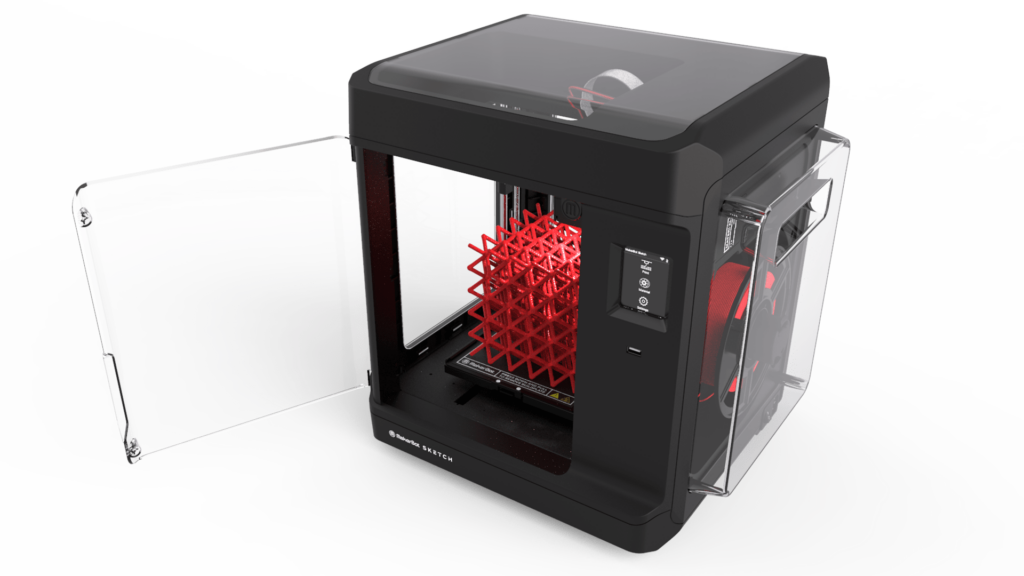

FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is a 3D printing technology that works by laying down successive layers of molten material to build up a 3D object.
It is one of the most widely used 3D printing processes due to its affordability, accessibility, and reliability. FDM works with a variety of materials, ranging from thermoplastics to composites and metal alloys.
FDM Printing Material: Tough and durable plastics, nylon, requires a heat bed and venting, rigid, strong
Best for Designs: Functional prototypes
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA (Stereolithography) is a 3D printing technology that works by curing liquid resin layer–by–layer to build up a 3D object. This is done with a laser beam that traces the layer pattern onto the resin.
SLA is a popular 3D printing technology due to its high accuracy and resolution, and the ability to print with a wide range of materials. It is also one of the fastest 3D printing processes, with some machines being able to print an object in just a few hours.
SLA Printing Material: Resins, these prints have the clearest details, and smoothest surface finishes of all 3D printers.
Best for Designs: Concept models, complex parts
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)

SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) is a 3D printing technology that works by heating and sintering layers of powder material to build up a 3D object.
It is a popular 3D printing technology due to its affordability and ability to produce strong and detailed parts. SLS is particularly well–suited for prototyping and low–volume production of complex geometries that cannot be produced with other 3D printing technologies.
SLS Printing Material: Nylon, thermoplastics, lightweight, strong, flexible, and stable against impact, chemicals, UV light, water, or dirt.
Best for designs: Medical devices, engineering prototypes, and end-use parts

